Then and Now: The Evolution of Mobile Medical Imaging
- April 18, 2023
- Posted in Excelsius™ Technology
On November 8, 1895, physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen became the first person to observe electromagnetic radiation in wavelength range. He named what he observed X-rays because of their unknown nature.1
The discovery instantly revolutionized the field of physics and medicine. The possibilities were immediately recognized and, in less than a year, X-ray imaging systems were being used for medical purposes.
X-rays are now one of the most common ways to view and monitor internal structures noninvasively and painlessly.
The Next Steps with Excelsius3D™
In the last 30 years, innovations in X-ray imaging technology have allowed medical professionals to use X-rays to significantly advance patient care.
Yet, despite recent technological advancements, mobile imaging systems have remained bulky and cumbersome, and often only meet a singular need during a procedure.
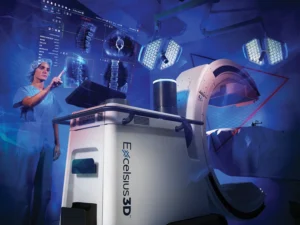
Globus Medical wanted to meet the needs of continually developing medical practices with an intelligent 3-in-1 imaging solution, Excelsius3D™.
Excelsius3D™ offers one solution for cone-beam CT, fluoroscopy, and digital radiography in one compact mobile unit, eliminating the need for multiple intraoperative imaging systems in the OR. Excelsius3D™ functions as an elite, standalone imaging unit or as an elegant extension of the Excelsius™ Ecosystem with automatic image registration for all three ExcelsiusGPS™ navigation workflows.
Excelsius3D™ is not CE marked and is not available in all regions. Contact your local Globus Medical representative to learn more.
Medical Imaging Timeline
1895
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovers X-rays.
1896
X-ray imaging systems are used for medical purposes for the first time.
1909
Friedrich Dessauer designs his “Blitzapparat,” an X-ray device that captures images in a few milliseconds, as opposed to several minutes.
1920s-1930s
Fluoroscopes are used in early X-ray rooms but without radiation awareness and protection.
1955
Philips introduces the BV 20, the first portable X-ray image intensifier-based “C-arm” for intraoperative 2D imaging.
1970s
The concept of radiology grows at a staggering pace: applications for imagery of every part of the body become possible. Image quality is enhanced, and radiation doses are reduced to minimal amounts.
1975
Sir Godfrey Hounsfield performs the first 3D CT visualization with cross-sectional images.
1977
Siemens unveils SOMATOM, the first full-body CT system.
1994
Ziehm develops the first mobile C-arm as a compact unit.
2000s
The age of preventative medicine begins, where CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds are utilized to diagnose an issue before it becomes life threatening.
2001
GE Healthcare releases Discovery LS, the first commercially viable PET-CT scanner that incorporates a 4-slice CT scanner.
2006
Medtronic develops the portable O-arm® with cone-beam CT for the first intraoperative 3D visualization. Ziehm designs the Vision FD with a flat panel that processes high-quality images without distortion.
2008
Medtronic integrates O-arm® and StealthStation® for intraoperative 3D navigation.
2009
Philips releases the Veradius Unity system, a compact mobile C-arm with a flat detector.
2015
Medtronic introduces O-arm® O2 with small-scale feature updates such as a slightly larger field of view and low dose scans.
2022
Globus Medical launches Excelsius3D™, the first 3-in-1 imaging system with 3D cone-beam CT, 2D fluoroscopy, and 2D digital radiography capabilities. Globus Medical integrates Excelsius3D™ with the ExcelsiusGPS™ robotic navigation platform.
Evolving the Future
When it comes to technological advancements, there are two main avenues of approach: iterative development and evolution.
Many existing imaging systems are iterations of older models, allowing them to maintain all the strengths of the original systems with some newer features to meet intraoperative imaging demands. However, the biggest disadvantage of this type of iterative development is the inability to modernize.
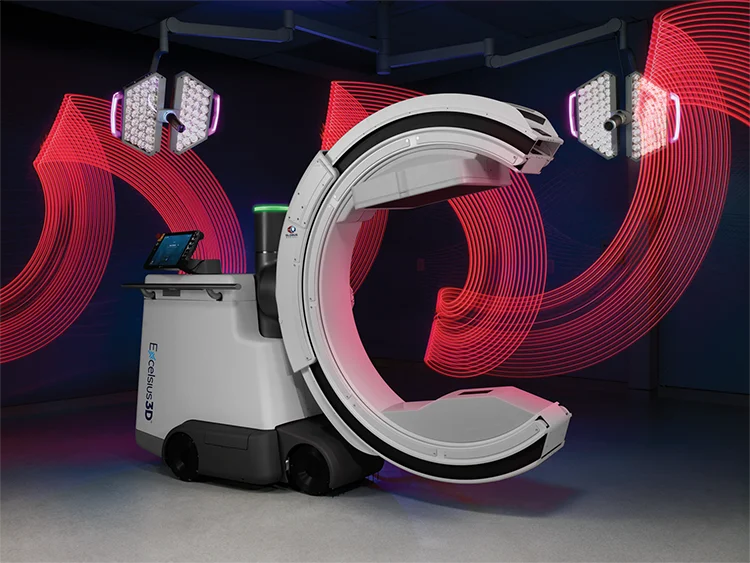
Excelsius3D™ is not an iteration of existing technology. It is an intelligent imaging system, moving toward a true evolution in medical imaging technology. The greatest strength of this evolution is the introduction of three imaging modalities in one system providing an innovative solution that current medical imaging systems do not provide.
Globus Medical approached this evolution by creating a design team of surgeons and engineers dedicated to addressing existing imaging concerns through lateral thinking. The result was a compact footprint and the elimination of a separate viewing station, which amplifies the system’s agility and usability.
But it did not stop there. The design team took things a step further with innovative applications such as haptic-response motion, omnidirectional wheels, and smart position memory, which offers unmatched imaging adaptability and maneuverability.
This is the kind of technology to truly transform patient care.
Questions about Exclesius3D™?
1 Nüsslin F. Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen: the scientist and his discovery. Phys Med. 2020; 79: 65-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.10.010.